SEBO662 AR+ NTCC?人皮脂腺細胞雄激素受體穩轉株-BioVector NTCC質粒載體菌株細胞蛋白抗體基因保藏中心
- 價 格:¥798950
- 貨 號: NTCC?-SEBO662 AR+
- 產 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培養物保藏中心
- 聯系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
電話:400-800-2947 工作QQ:1843439339 (微信同號)
郵件:Biovector@163.com
手機:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注冊
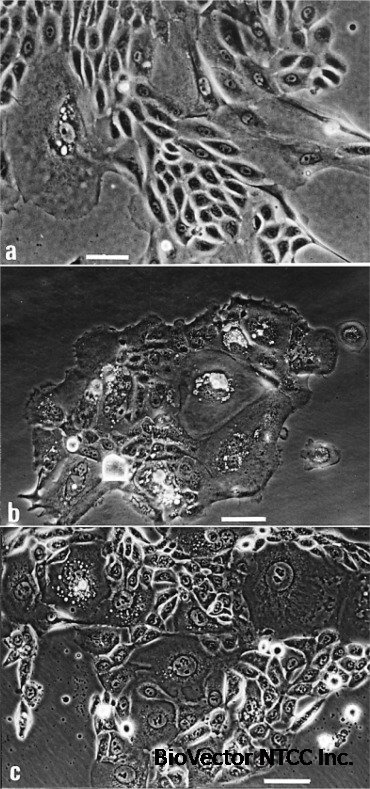
The NTCC? SEBO662 AR+ cell line is a human cell line derived from sebocytes (cells of the sebaceous glands in the skin), which has been engineered to stably express a functional Androgen Receptor (AR).
Here's a breakdown of its key features and why it's important in research:
Origin and Background:
SEBO662: The base cell line, SEBO662, is an immortalized human sebocyte cell line. Sebocytes are the cells responsible for producing sebum, the oily substance that lubricates and protects the skin. This base line was established by immortalizing human sebocytes, often through transduction with viral oncogenes like Human Papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) E6 and E7 proteins.
AR+ (Androgen Receptor Positive): The "AR+" designation indicates that this specific variant of the SEBO662 cell line has been genetically modified to constitutively express a functional Androgen Receptor. The original SEBO662 might have low or absent endogenous AR expression, making it less responsive to androgens.
Why the AR+ modification is crucial:
Androgens (male hormones like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone - DHT) are key regulators of sebaceous gland function. They stimulate sebum production and sebocyte differentiation. In conditions like acne, an overactive androgen signaling pathway in sebaceous glands contributes to hyperseborrhea (excessive sebum production) and inflammation.
Therefore, creating an AR+ version of the SEBO662 cell line provides a highly relevant in vitro model for studying:
Androgen-mediated sebocyte biology: It allows researchers to investigate how androgens directly influence sebocyte proliferation, differentiation, and lipid synthesis.
Mechanisms of sebum production: By treating SEBO662 AR+ cells with androgens (e.g., DHT), researchers can stimulate lipid accumulation and study the molecular pathways involved in sebum synthesis.
Pathogenesis of acne and seborrheic dermatitis: This cell line is invaluable for understanding the role of androgen signaling in these common skin conditions, which are characterized by sebaceous gland dysfunction.
Drug screening for dermatology: It serves as a model to test potential therapeutic agents that aim to modulate androgen receptor activity or inhibit sebum production, offering a way to screen for new treatments for acne and related disorders.
Key Characteristics and Applications of SEBO662 AR+:
Androgen Responsiveness: When treated with androgens (like DHT), SEBO662 AR+ cells show:
AR nuclear translocation: The androgen receptor moves from the cytoplasm into the nucleus, where it can bind to DNA and regulate gene expression.
Modulation of androgen-sensitive genes: Expression of genes known to be influenced by androgens (e.g., RASD1, GREB1, MUC1/EMA, AQP3, FADS2) is altered.
Increased lipid synthesis: They accumulate triglycerides in lipid droplets, mimicking sebum production.
Morphological changes: Cells may increase in size, indicative of differentiation.
Induction of differentiation: Androgens can push immature sebocytes towards a more differentiated, lipid-producing phenotype.
Model for Acne and Seborrhea Research: It's a gold standard in vitro model for evaluating:
Anti-androgenic compounds.
Sebostatic agents (substances that reduce sebum production).
Anti-inflammatory agents relevant to sebaceous gland inflammation.
The effects of various cosmetic ingredients or pharmaceutical compounds on sebocyte function.
Drug Metabolism Studies: Can be used to study how sebocytes metabolize hormones or drugs.
BioVector NTCC質粒載體菌株細胞蛋白抗體基因保藏中心
www.biovector.net
- 公告/新聞